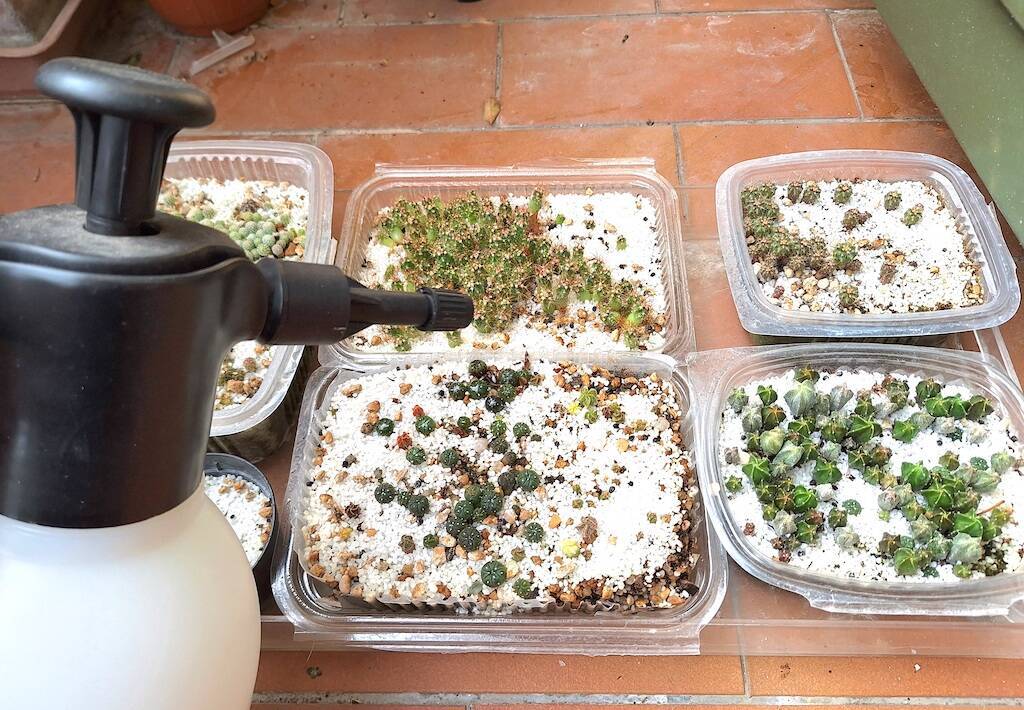
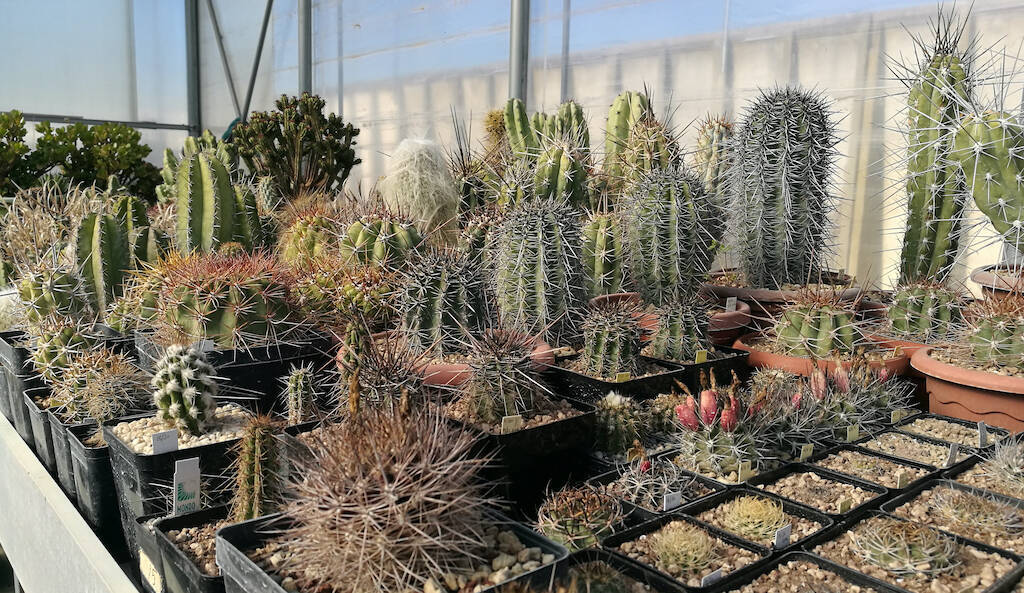
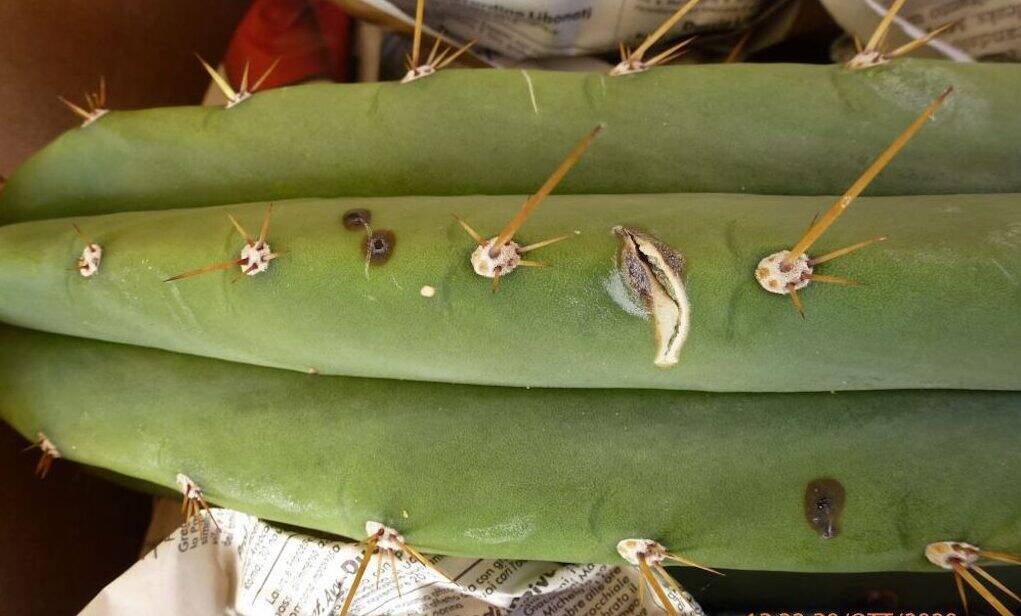
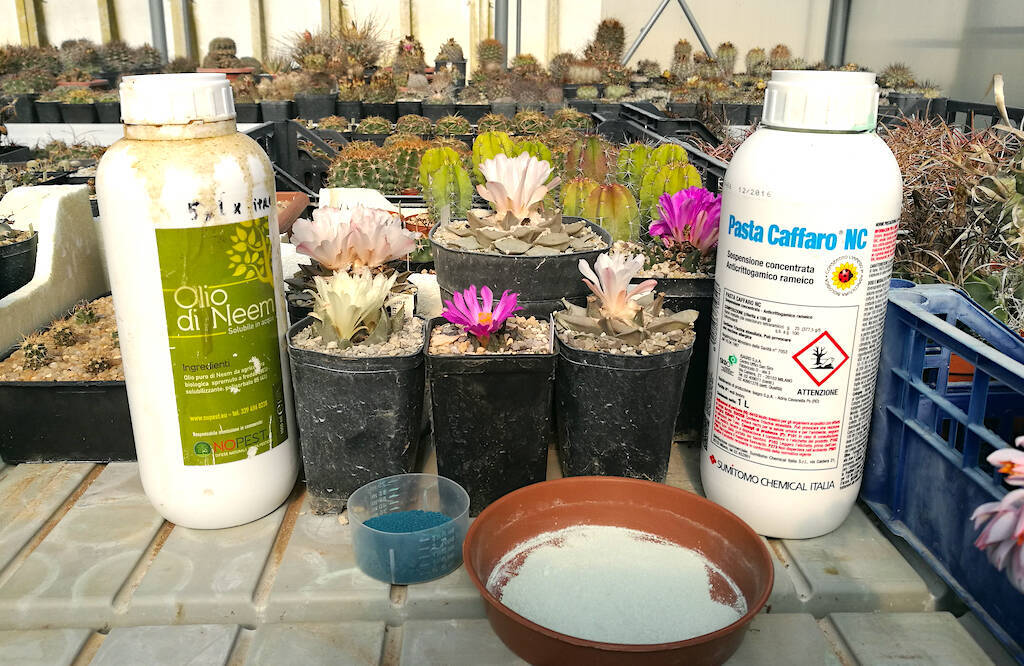
With the beginning of autumn almost all succulent and cacti begin to prepare for the vegetative stasis which will last until February/March. In the winter months, cacti (with some exceptions such as Melocactus, Discocactus and epiphytes such as Epiphyllum) and many succulents (with the exception of those originating from the southern hemisphere or areas such as Madagascar) stop growth and go dormant to recover energies and be able to flourish during the following season. In these months the plants should be kept cold and should not be watered. However, it is useful to carry out some preventive treatments to prevent the formation of mold or fungi during these months, thanks to the winter humidity, which, when the temperature start to rise, triggers rot. Warning: preventive treatments with chemical products can be useful but do not necessarily have to be carried out. It is simply a preventive measure, since the best form of defense is always the spartan cultivation of plants accompanied by a good exchange of air during autumn and winter. There are growers who limit these treatments to the essentials, perhaps favoring products with a low environmental impact (I myself have adopted this decision for years) and growers who abuse chemical products in the hope of thus making their plants invulnerable to animal parasites, fungi and mold.
In this article, which completes what has already been explained in other articles (which you will find thanks to the internal links) we see what is advisable to do in these weeks to protect the plants and limit losses due to rot or parasites as much as possible. (…)
Per proseguire nella lettura dell'articolo Accedi o Abbonati
To continue reading the article LogIn or Subscribe