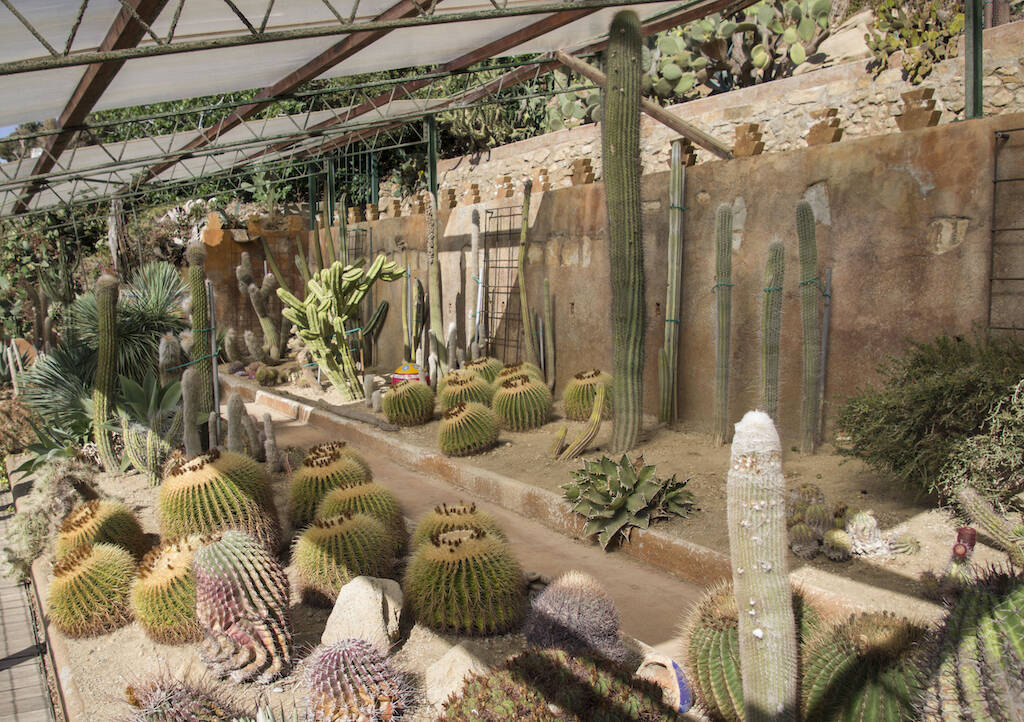
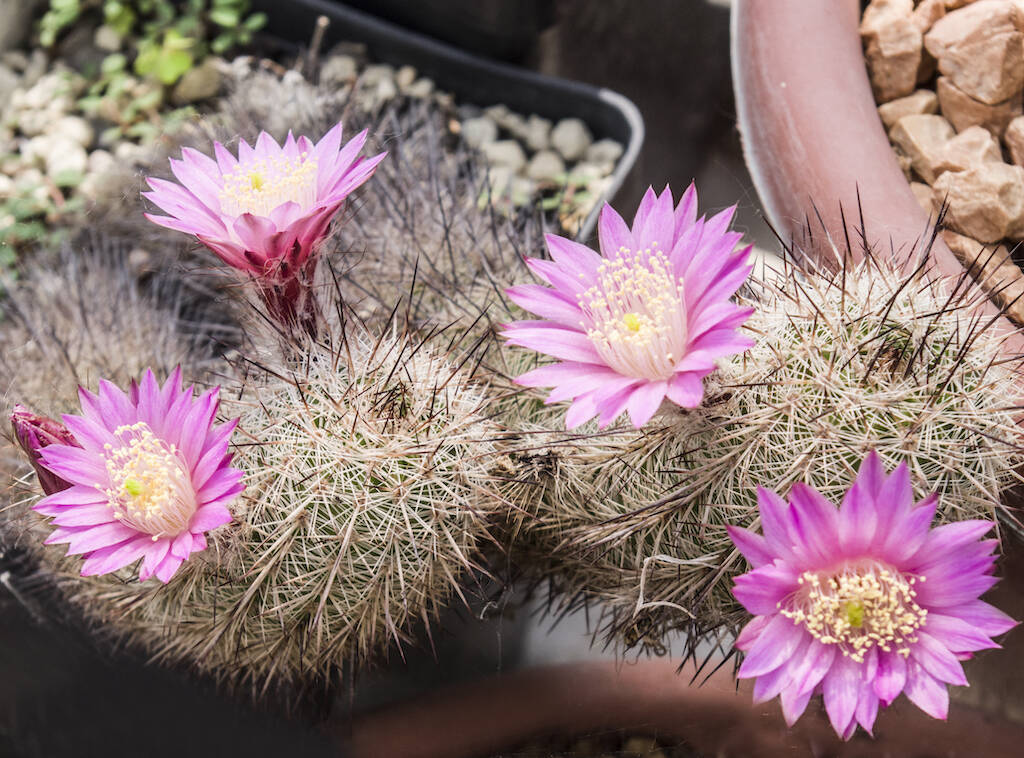
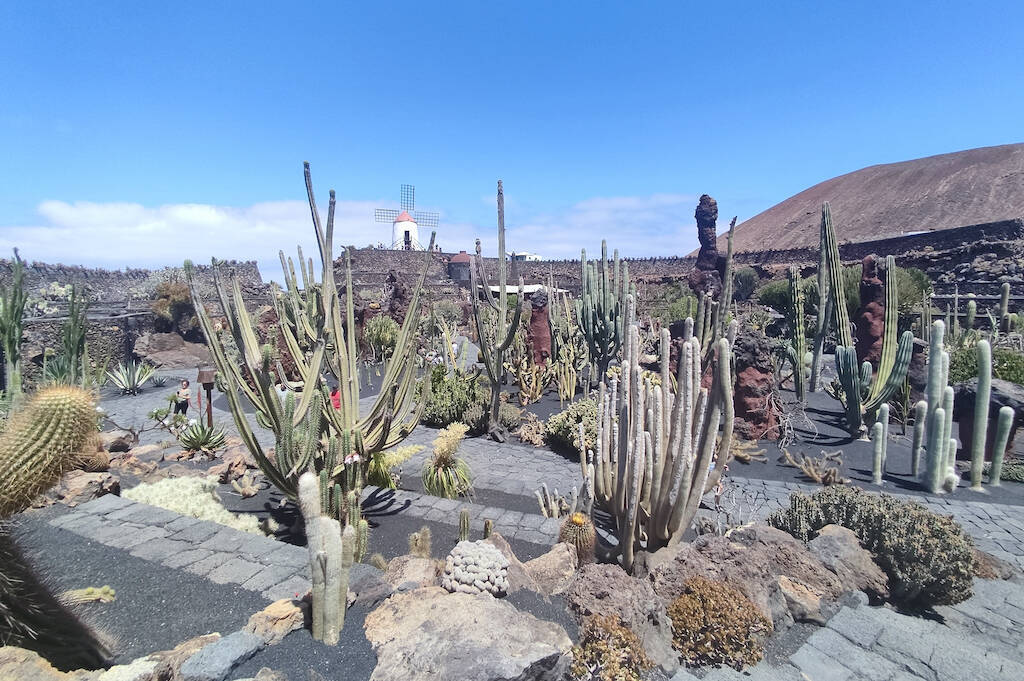
The world of succulent plants is extremely vast. It follows that the cultivation needs of individual succulents can vary considerably from family to family and from genus to genus. With a concrete example, a cactus (plant belonging to the Cactaceae family) has extremely different cultivation needs compared to an Adenium obesum (succulent plant belonging to the Apocynaceae family). Likewise, large differences in cultivation can occur within the same family or between different genera of a single family. Here too is an example: an Ariocarpus (genus belonging to the Cactaceae) requires a cultivation regime, understood as substrate, watering, etc. very different from an Echinopsis (genus always belonging to the Cactaceae).
Without dwelling too much on the broad field of plant classification (here, if you want, you will find an article dedicated to this topic) and taking it for granted that the term “succulent plants” refers both to cacti and to many other succulent botanical families whose specimens have a different appearance from any other cactus, we are addressing a very “heartfelt” topic among novice growers. Even the grower who boasts a good knowledge of a given family, however, may find the following article useful, which recommends succulent plants (belonging to various botanical families) that are less demanding, more robust and simple to grow and therefore more suitable for those who are only now approaching the world of succulents. (…)