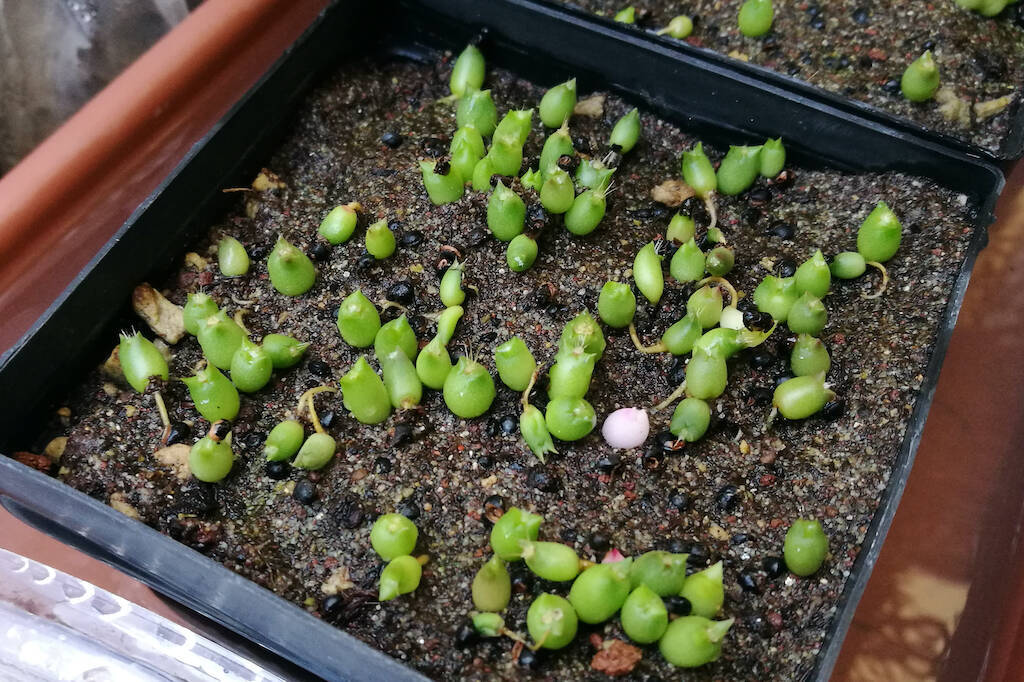
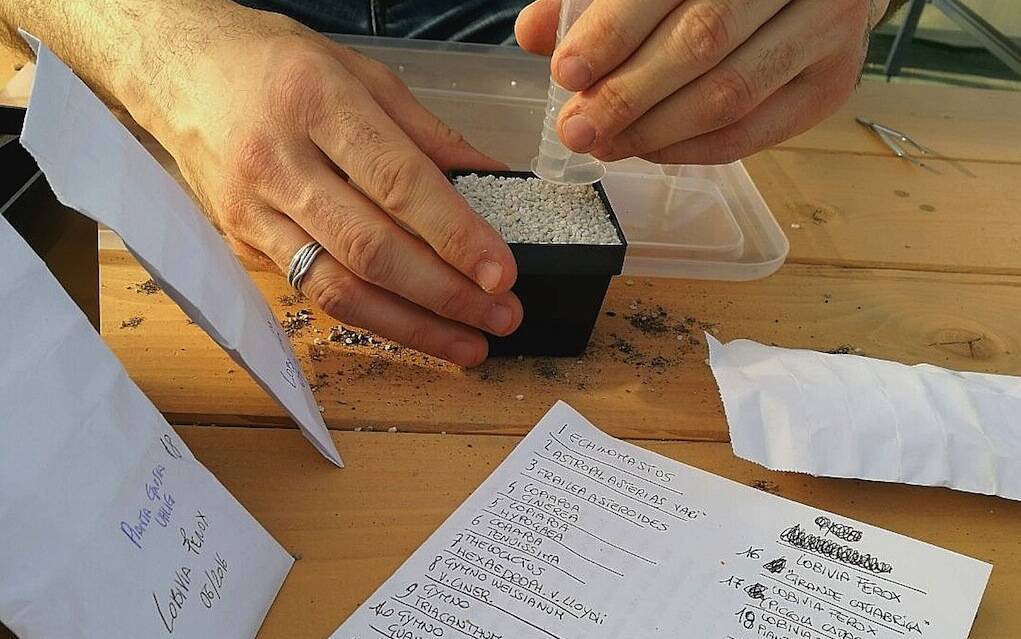
Reproducing cacti starting from seeds is one of the best ways to get to know these plants in depth. Through sowing we can in fact observe the entire life cycle of the plant, from birth to the production of the first flower, to aging and death. Without forgetting the great satisfaction that the birth of seedlings is able to offer to those who practice sowing for the first time as well as those who have practiced it every year for decades. Not to mention the first flower: getting to see that the plant that we have given birth from a small seed, after two years or after twenty years depending on the species, finally opens its flower… it is priceless, there’s little to do. But before getting to all this – with regard to the sowing procedure, remember that on this site there is an entire section with at least fifteen articles dedicated to this topic at this link – you need to get the seeds. Banal, obvious. But without those you go nowhere. And there are two ways to get the seeds: buy them from specialized retailers (now almost exclusively online) or produce them with the manual pollination of your own plants. Or… simply collect the fruits that our plants have produced thanks to some pollinating insect, accepting the fact that two plants not of identical species may have been pollinated (and therefore we will be dealing with future hybrids), clean the fruits, store them and sow them in the spring.
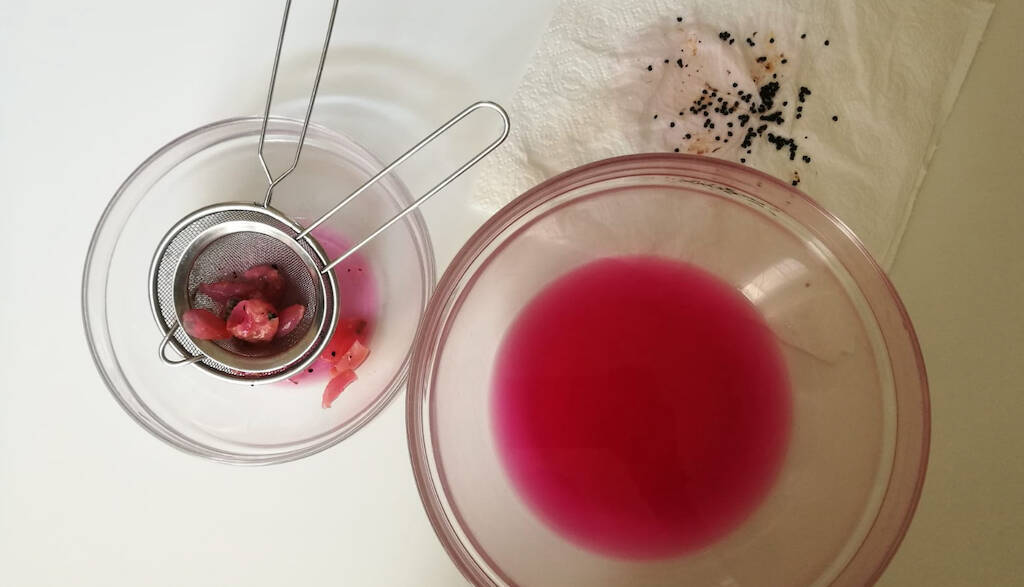
In this article and in the related video we see how to clean and prepare the seeds for storage for future sowing. We sholud always remember that the seeds must be stored correctly, on pain of deterioration of the seeds and the consequent drastic drop in germinability. (…)
Per proseguire nella lettura dell'articolo Accedi o Abbonati
To continue reading the article LogIn or Subscribe