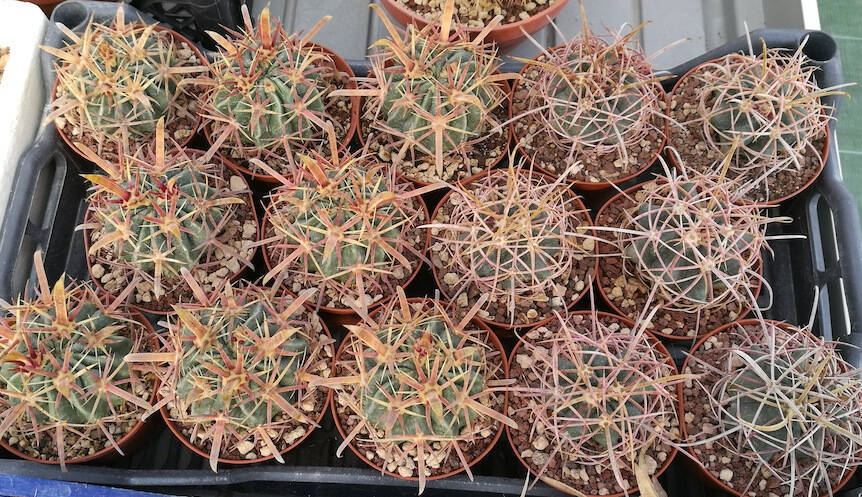
I generally start repotting from mid-December onwards, to finish within the first few months of the new year. This year, considering the number of plants I sow that need repotting, I started well in advance. Despite the still high temperatures for the period, in fact, the plants are already in stasis and it is possible to proceed without problems. The repotting period is one of the most debated topics, together with the composition of the growing soils: there are those who repot only plants in vegetation, those only in spring, those during the winter and those who repot at any time of the year. Let’s say that there isn’t a fixed rule: over the years, I have repotted practically in all seasons, according to needs, and I have never encountered any problems. The important thing is to stick to that only really useful precaution which is to avoid watering immediately after repotting. It is necessary to give the damaged or cut roots time to heal in dry soil during repotting, so as to avoid the risk that they may trigger rot. The rest is a matter of choices. Personally I prefer to repot and change the soil to the plants during the winter season, or in any case when the cacti and succulents are in vegetative stasis, for example just before spring, so that several weeks elapse between repotting and the first watering. I’ve been following this “rule” for years and have never had a problem. Of course, it may happen that some plants find it difficult to restart after repotting, to the point of being stuck even for a whole year, but this can happen by repotting at any time. Let’s not forget that repotting is in any case a significant “stress” for plants. This is also why I prefer winter, when the cacti are at rest and the effects of repotting are less “traumatic”.
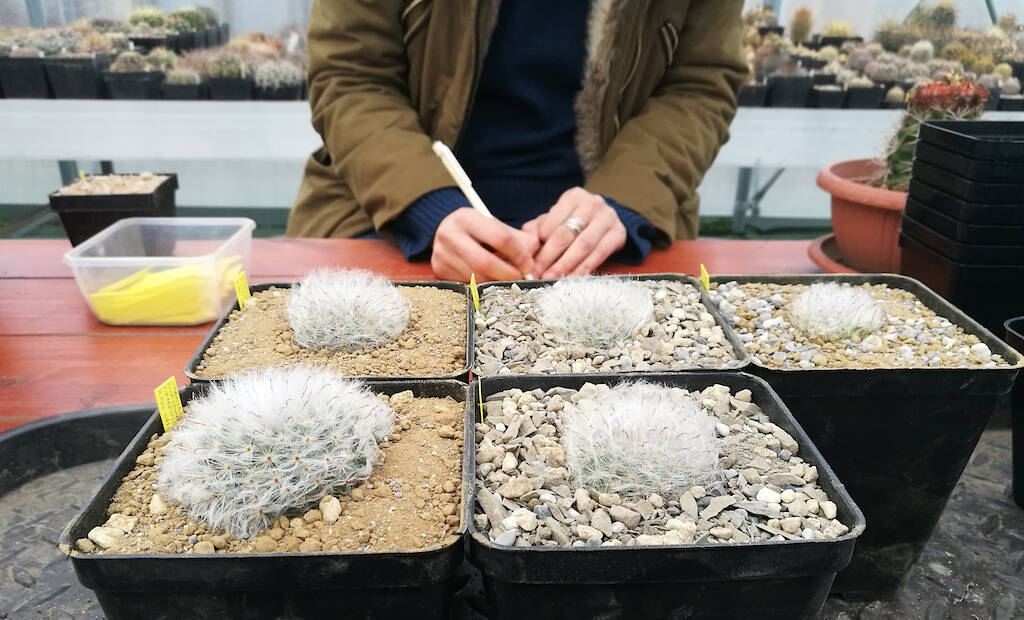
Let’s explore the topic of repotting and substrates for cacti, in particular the “standard” soil based on pumice, lapillus and peat in equal parts, in the following article. (…)
Per proseguire nella lettura dell'articolo Accedi o Abbonati
To continue reading the article LogIn or Subscribe